Anka VM Networking
Default Networking Configuration
Anka VMs, by default, use a shared networking configuration with the host. It’s a kind of NAT + DHCP. Every time you start/resume a VM, it gets assigned an IP that you can see with anka show VM command.
In order to access this VM from the host on which it’s running do the following.
ssh usr@vm_ip
Where usr is the user-created inside the VM.
Every Anka VM created using anka create command has a default user anka and password admin.
In order to access this VM from outside of the host it’s running, enable port forwarding.
Use anka modify command.
anka modify VM add port-forwarding -g 22 ssh
When the port forwarding rule is successfully added, you will see the following in the anka show vmname output.
port_forwarding
+--------------+-------------+------------+---------+-----------+
| guest_port | host_port | protocol | name | host_ip |
+==============+=============+============+=========+===========+
| 22 | 10001 | tcp | ssh | 0.0.0.0 |
+--------------+-------------+------------+---------+-----------+
Access it from ouside the host with ssh anka@hostip -p host_port
Changing network configuration for Anka VMs
Following command is used to administer network parameters of the VM.
anka modify set network-card [OPTIONS] INDEX
Options are:
-t, --type [shared|host|bridge|disconnected]
-b, --bridge TEXT host interface name to bridge with (Wi-Fi is not supported)
-m, --mac TEXT specify fixed MAC address
-n, --no-mac deassign fixed MAC address
INDEX is always 0 since Anka doesn’t support more than 1 NIC per VM now.
Shared type
It is the default network type operating as NAT + DHCP. Every VM after the start/resume gets an IP address assigned by the internal DHCP server in range 192.168.64.2 - 192.168.64.254.
In order to access the host from inside the VM use the IP address of 192.168.64.1 (or 192.168.128.1 in host-only mode). Programs inside a VM can access external networks (outside the host) and the Internet directly. Also, other VMs on the host are also accessible. Software services can not be accessed directly from external networks. To access such services port forwarding should be configured on the host.
Host type
It is very similar to the shared one, but VMs get IP addresses from range 192.168.128.2 - 192.168.128.254 and can’t access external networks outside of the host.
Bridge Type
anka modify VM set network-card 0 -t bridge
Use this to configure bridged networking mode for Anka VMs. VM can be bridged to Ethernet interfaces only (including USB dongles). WiFi interfaces are not supported yet. The interface to bridge can be assigned automatically (default) or specified in VM config.
anka modify VM set network-card 0 -t bridge -b en0
Or default interface can be specified on per-user basis:
anka config bridge_name en0
Since anka settings can be overwritten with env variables, the following will work too.
ANKA_BRIDGE_NAME=en0 anka start VM …
VMs with this network type is visible in the network as independent nodes. VMs can be accessed from external networks directly. Since anka create process leaves guest macOS in “Using DHCP” mode, external DHCP server could be needed to get network up immediately, or manual IP address assignment will be needed.
Disconnected type
With this type of networking the VMs see only “disconnected” ethernet cable. No network communications is available. This mode is pretty much like removal of entire NIC from a VM’s configuration.
anka modify VM delete network-card 0
MAC addresses
Current Anka implementation uses dynamically assigned MAC addresses. These addresses are being allocated from a pool and can’t be specified directly in VM’s config or so, regardless of the --mac option in the modify command. The MAC addresses could be reused between different VMs during a time, so VMs can’t be identified from the network by MAC address.
There is the ability to assign static internal MAC address (visible inside VM only) with the --mac option. This feature is used if it’s needed to make different VMs, e.g. clones of the same VM, to act as the same network node, but in this case, there could be collisions when several instances of such VMs run on the same host. Static MAC address is being translated to dynamic one and vice-versa during a packet routing.
Static IP
Anka 2.2 supports Static IP on VMs running on Catalina hosts (the guest OS can be any supported macOS version). To use static IP addresses follow the following steps.
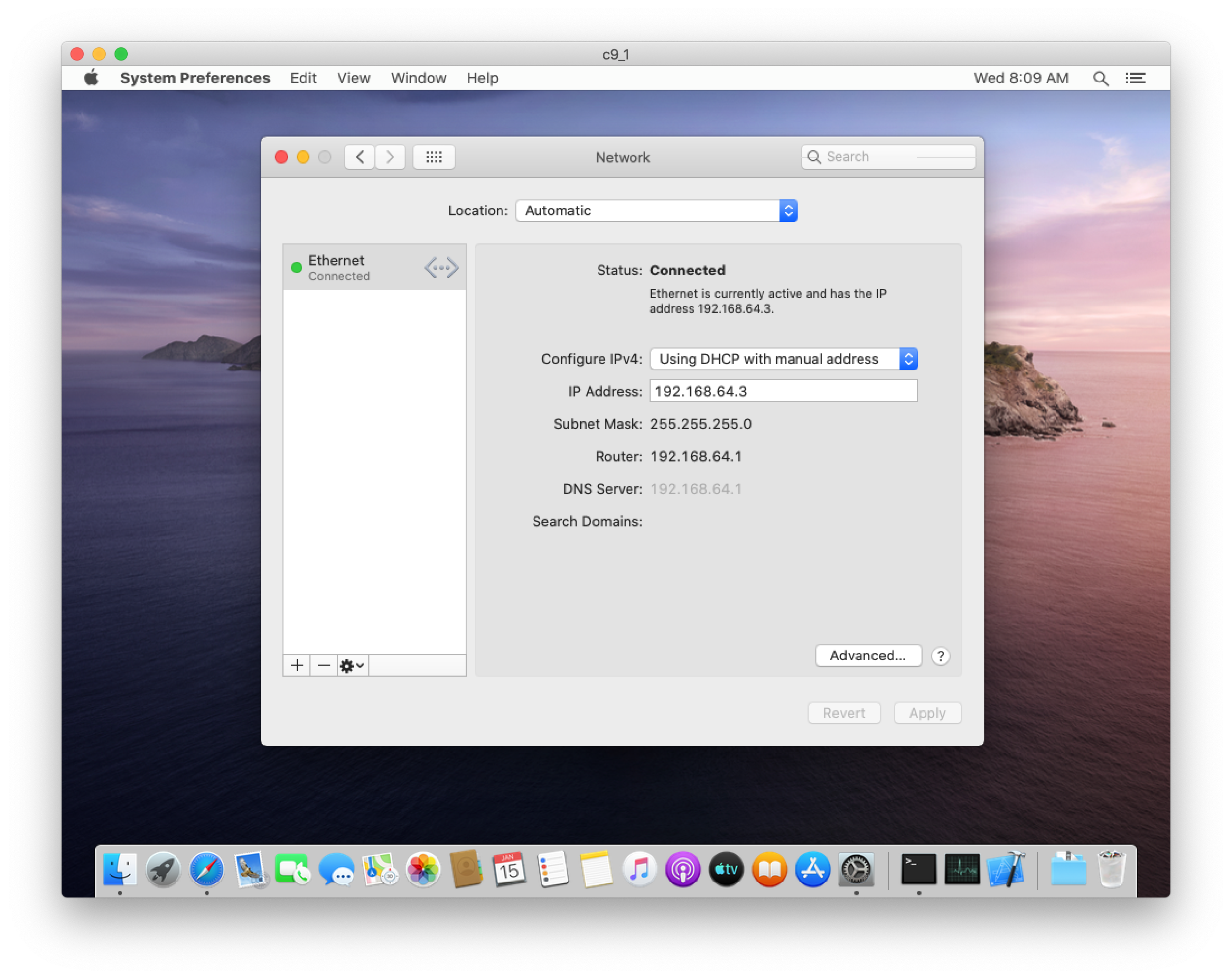
If the network-card setting on the VM is set to bridge, the IP address setting is driven by external network configuration.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Glad to hear it! Please tell us how we can improve.
Sorry to hear that. Please tell us how we can improve.